Geography
Armenia is geographically located in the South Caucasus on the south-eastern part of Europe. To the West it borders with Turkey, in North with Georgia, in East with Azerbaijan and in South with Iran.
Nearly 90% of the territory is located between 1000 and 2500 meters above the sea level. The maximum altitude is 4090m (Aragats) and the minimum level is 375m (Canyon Debed).
The highest point is the historical Mountain Ararat with its 5160 meters, which is in the territory of present day Turkey. There are many dead volcanoes including Aragats and Porak. The volcanic landscapes are frequent and they sometimes give spectacular scenery (basalt in the region Jermuk, caves dug in the tuff in Khndzoresk).
There are more than 200 rivers and hundreds of lakes in Armenia. The largest river is Araks, which forms the border with Iran and Turkey.
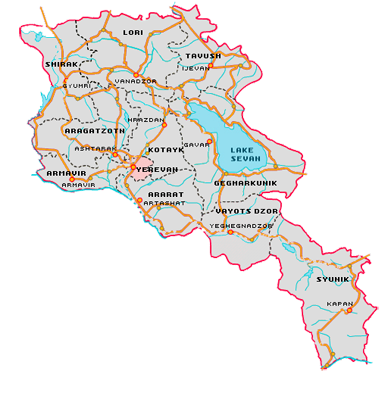
The Armenian landscape is also characterized by its lakes including Lake Sevan, which is 1262.2km2 and is located 60km east to Yerevan. This is the second largest lake in the world after the Titicaca in Peru situated at an altitude of 1 898m.
The country is divided into ten regions including the capital Yerevan. These regions are divided into 926 communities (48 urban and 865 rural) which are also subdivided into thousands of areas.